We have been assigned to elog our internal assessment questions where the goal is to achieve learning driven through searchable information, particularly with regard to making original contributions and avoiding plagiarism from the searched work.
Here is my attempt of doing so.Our question paper has been prepared as to assess our ability in our clinical postings regarding " Patient clinical data analysis" to develop our competancy in comprehending clinical data including history, clinical finding, investigations and come up with a diagnosis and treatment plan.
NOTE: All the questions in the below question paper had been some of cases in our medical college in this past month.
1st question:
A bone density test is used to measure bone mineral content and density. It may be done using X-rays, dual-energy
X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA or DXA), or a special CT scan that uses computer software to determine bone density of the hip or spine.
2nd ans:
Myxedema (crisis) coma is
a loss of brain function as a result of the severe, longstanding low level of thyroid hormone in the blood (hypothyroidism). Myxedema coma is considered a rare life-threatening complication of hypothyroidism and represents one of the more serious sides of thyroid disease.Initial steps in therapy include airway management, thyroid hormone replacement, glucocorticoid therapy, and supportive measures.
5th ans:
Beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers are first-line agents for rate control in AF. These drugs can be administered either intravenously or orally. They are effective at rest and with exertion. Intravenous diltiazem or metoprolol are commonly used for AF with a rapid ventricular response.
6th ans:
Megaloblastic anemia is
a form of anemia characterized by very large red blood cells and a decrease in the number of those cells. Anemias are blood disorders that occur when the body has fewer red blood cells than normal. Red blood cells carry oxygen throughout the body using a protein called hemoglobin.
8th ans:
Patients with acute pancreatitis lose a large amount of fluids to third spacing into the retroperitoneum and intra-abdominal areas. Accordingly, they require
prompt intravenous (IV) hydration within the first 24 hours. Especially in the early phase of the illness, aggressive fluid resuscitation is critically important.
9th ans:
An upper motor neuron lesion is a lesion of the neural pathway above the anterior horn of the spinal cord or motor nuclei of the cranial nerves. A Lower motor neuron lesion is a lesion which affects
nerve fibers traveling from the anterior horn of the spinal cord to the associated muscle.
- intractable hyperkalaemia;
- acidosis;
- uraemic symptoms (nausea, pruritus, malaise);
- therapy-resistant fluid overload;
- chronic kidney disease (CKD) stage 5.
11th ans:
Sucralfate (complex salt of sucrose aluminum hydroxide and sulfate) has a positive charge and binds to the negative charge of the ulcer base to form a gel, which acts to effectively plug the ulcer base and to prevent worsening of the gastritis.
Besides the local and systemic symptoms, clinical renal manifestations vary from mild proteinuria, haematuria, pigmenturia to acute renal failure. Bites by haemotoxic snakes and myotoxic snakes are the common causes of renal involvement especially acute renal failure.
13th ans:
The most common cause of portal hypertension is
cirrhosis, or scarring of the liver. Cirrhosis results from the healing of a liver injury caused by hepatitis, alcohol abuse or other causes of liver damage. In cirrhosis, the scar tissue blocks the flow of blood through the liver and slows its processing functions.
14th ans:
A few of the common physical traits of Down syndrome are
low muscle tone, small stature, an upward slant to the eyes, and a single deep crease across the center of the palm.15th ans:
- Acute renal failure (rapid loss of kidneys' ability to remove waste and help balance fluids and electrolytes in the body)
- Chronic glomerulonephritis.
- Chronic kidney disease.
- Heart failure or pulmonary edema (fluid buildup in the lungs)
- End-stage renal disease.
- Rheumatoid arthritis of the neck.
- Whiplash injury or other cervical spine trauma.
- Spinal infections.
- Spinal tumors and cancers.
Young-onset hypertension is a common condition that increases all-cause mortality and results in subclinical organ damage early in its natural history. Epidemiological studies suggest that early-life factors are important and should be addressed by public health policies to reduce cardiovascular disease later in life.
Referral of selected patients to secondary care (is suggested as it permits more detailed assessment, evaluation of subclinical organ damage, and investigation of secondary causes of hypertension. This can allow more personalized management given the limitations of current risk-based approaches in this population. Early intervention with medication in young, mild hypertensives (blood pressure, >140/90 mm Hg) free of cardiovascular disease could be considered following a 1-year trial of lifestyle modification.
7th ans:
The most common cause of ascites is
cirrhosis of the liver. Drinking too much alcohol is one of the most common causes of cirrhosis of the liver. Different types of cancer can also cause this condition. Ascites caused by cancer most often occur with advanced or recurrent cancer.
























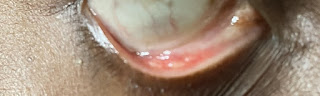

Comments
Post a Comment